History Of The Northwest Territories on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of the Northwest Territories covers the period from thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands that encompass present-day
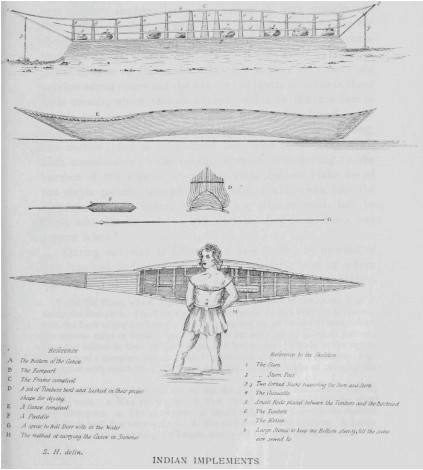 Long before the Europeans arrived, Inuit and First Nations peoples inhabited the land area which became the Northwest Territories. Native Inuit included the Mackenzie,
Long before the Europeans arrived, Inuit and First Nations peoples inhabited the land area which became the Northwest Territories. Native Inuit included the Mackenzie,
 Franklin's
Franklin's
 After the
After the
 In June 1899, negotiation began on Treaty No. 8, which covered 840,000 square kilometres in the North-West Territories. It was an agreement between the Canadian Government and the Dene groups in the area in question; in return for their willingness to share their land with non-Natives, the Dene would receive medical and educational assistance, as well as treaty payments. The Canadian Government and the various Dene groups, including
In June 1899, negotiation began on Treaty No. 8, which covered 840,000 square kilometres in the North-West Territories. It was an agreement between the Canadian Government and the Dene groups in the area in question; in return for their willingness to share their land with non-Natives, the Dene would receive medical and educational assistance, as well as treaty payments. The Canadian Government and the various Dene groups, including
 In 1906, the official name dropped the hyphen, changing to "Northwest Territories".
On May 15, 1912, parts of the Northwest Territories were given to Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
In 1906, the official name dropped the hyphen, changing to "Northwest Territories".
On May 15, 1912, parts of the Northwest Territories were given to Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
 During
During
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
were inhabited for millennia by several First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
. European explorers and fur traders began to explore the region since the late-16th century. By the 17th century, the British laid claim to both the North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Due to the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact boundarie ...
and Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
; and granted the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
a commercial fur trade monopoly over the latter region.
After the Deed of Surrender
The Deed of Surrender or Rupert's Land and North-Western Territory Order is an 1870 British order in council that transferred ownership of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory from the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) to the newly created Do ...
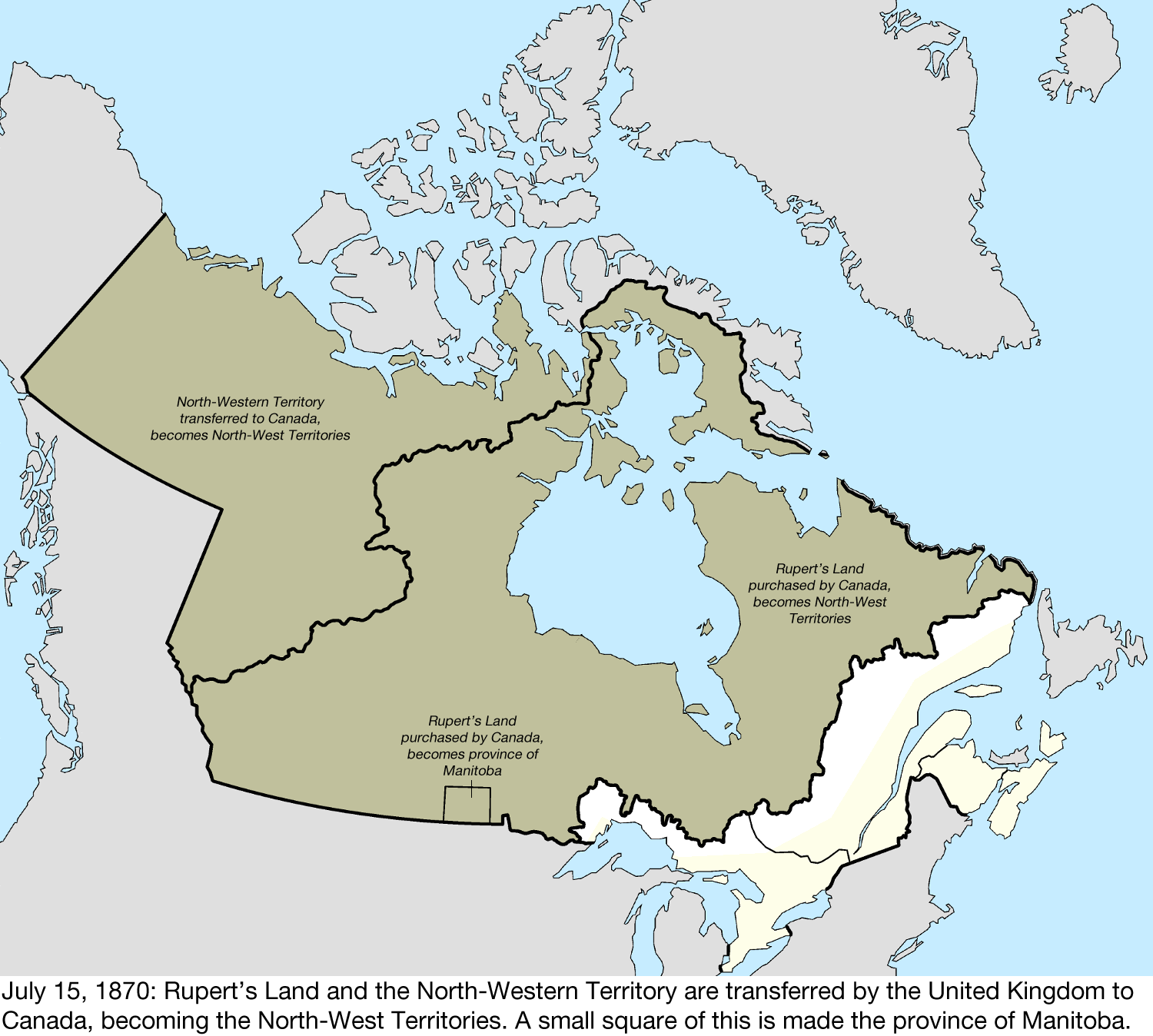
was enacted on 23 June 1870, the United Kingdom transferred the North-Western Territory and Rupert's Land to the government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
, with most all of the newly transferred territory administered as the ''North-West Territories.'' The hyphen was later dropped after the passing of the ''Northwest Territories Act'' in 1906. The territory reached its largest size in 1880, after the British Arctic Territories
The British Arctic Territories were a constituent region of British North America, composed of islands to the north of continental North America. They are now known as the Arctic Archipelago.
The British claim to the area was based on the di ...
were transferred from the United Kingdom to Canada, and incorporated into the North-West Territories. However, the size of the territory was reduced several times during the late 18th- and early 19th centuries. Major adjustments to the boundary of the territory during this period includes severing of its western portions to form the Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
in 1898, severing its south-western portions to form the provinces of Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
in 1905, and transferring its remaining lands south of the 60th parallel north
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as ...
and the District of Ungava to the provinces of Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, and Quebec in 1912.
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
era, a number of responsibilities were devolved from the federal to territorial government, with the territory's capital transferred from Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
to Yellowknife
Yellowknife (; Dogrib: ) is the capital, largest community, and only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the ...
in 1967. During the 20th century, the federal government entered into land claim negotiations with the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, (Inuktitut syllabics: , meaning "Inuit are united in Canada") previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Eskimo Brotherhood of Canada), is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit acro ...
. The resulting land claim negotiations saw the eastern portions of the territory separated from the rest, forming the territory of Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
in 1999.
Early history
 Long before the Europeans arrived, Inuit and First Nations peoples inhabited the land area which became the Northwest Territories. Native Inuit included the Mackenzie,
Long before the Europeans arrived, Inuit and First Nations peoples inhabited the land area which became the Northwest Territories. Native Inuit included the Mackenzie, Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, Caribou
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
, and Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
nations. There were also many nations when the Europeans first arrived, among them the Yellowknives
The Yellowknives, Yellow Knives, Copper Indians, Red Knives or T'atsaot'ine ( Dogrib: ''T'satsąot'ınę'') are indigenous peoples of Canada, one of the five main groups of the First Nations Dene who live in the Northwest Territories of Canada. ...
, Chipewyan
The Chipewyan ( , also called ''Denésoliné'' or ''Dënesųłı̨né'' or ''Dënë Sųłınë́'', meaning "the original/real people") are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified ...
, Sekani
Sekani or Tse’khene are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group in the Northern Interior of British Columbia. Their territory includes the Finlay and Parsnip River drainages of the Rocky Mountain Trench. The ne ...
, Beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
, Nahanni, Dogrib, and Slavey
The Slavey (also Slave and South Slavey) are a First Nations indigenous peoples of the Dene group, indigenous to the Great Slave Lake region, in Canada's Northwest Territories, and extending into northeastern British Columbia and northwestern ...
.
Martin Frobisher's expeditions in the 1570s were the first recorded visits to the Northwest Territories by a European. In 1610, Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 160 ...
, while looking for the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
, landed briefly on the western shore of the bay that bears his name. His discovery opened the interior of the continent to further exploration. Other early explorers include Luke Foxe
Luke Foxe (or Fox) (20 October 1586 – c. 15 July 1635) was an English explorer, born in Kingston-upon-Hull, Yorkshire, who searched for the Northwest Passage across North America. In 1631, he sailed much of the western Hudson Bay before ...
, John Davis, Robert Bylot
Robert Bylot () was an English explorer who made four voyages to the Arctic. He was uneducated and from a working-class background, but was able to rise to rank of master in the English Royal Navy.
Voyages
Robert Bylot
First voyage, 1610� ...
, Thomas Button
Sir Thomas Button (died April, 1634) was a Wales, Welsh officer of the Royal Navy, notable as an explorer who in 1612–1613 commanded an expedition that unsuccessfully attempted to locate explorer Henry Hudson and to navigate the Northwest Pa ...
, George Weymouth
George Weymouth (Waymouth) () was an English explorer of the area now occupied by the state of Maine.
Voyages
George Weymouth was a native of Cockington, Devon, who spent his youth studying shipbuilding and mathematics.
In 1602 Weymouth was ...
, Thomas James
Thomas James (c. 1573 – August 1629) was an English librarian and Anglican clergyman, the first librarian of the Bodleian Library, Oxford.
Life
He was born about 1573 at Newport, Isle of Wight. In 1586 he was admitted a scholar of Winchest ...
, and William Baffin
William Baffin ( – 23 January 1622) was an English navigator, explorer and cartographer. He is primarily known for his attempt to find a Northwest Passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific, during the course of which he was the first Euro ...
.
Fur trade (17th– and 18th century)
In 1670, King Charles II granted a charter to the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading into Hudsons Bay, known as theHudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
(HBC). It included the Hudson's Bay watershed.
By the 1700s, European trade in the North-West Territories was dominated by two fur-trading companies, the Hudson's Bay Company, based in London, England, and the North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
based in Montréal. Fur trade explorer Peter Pond
Peter Pond (January 18, 1739 – 1807) was an American explorer, cartographer, merchant and soldier who was a founding member of the North West Company and the Beaver Club. Though he was born and died in Milford, Connecticut, most of his life ...
lead the way through the Methye Portage
The Methye Portage or Portage La Loche in northwestern Saskatchewan was one of the most important portages in the old fur trade route across Canada. The portage connected the Mackenzie River basin to rivers that ran east to the Atlantic. It wa ...
into the vast territory of the north-west where the rivers flowed north rather than east. In 1771, Samuel Hearne
Samuel Hearne (February 1745 – November 1792) was an English explorer, fur-trader, author, and naturalist. He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, actually Coronation Gulf, via the C ...
was the first European to reach the shore of the Arctic Ocean by an overland route via the Coppermine River. Further west and eighteen years later, in 1789, Alexander Mackenzie reached the Arctic Ocean. The river he navigated to get there now bears his name.
York Factory
York Factory was a settlement and Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) factory (trading post) located on the southwestern shore of Hudson Bay in northeastern Manitoba, Canada, at the mouth of the Hayes River, approximately south-southeast of Churchill. Yo ...
later served as the Hudson's Bay Company's headquarters. The HBC depended on the furs coming to York Factory. The North West Company competed with the HBC by travelling throughout the territory obtaining furs as they did so. Some of these trader explorers kept journals and had them published. Public interest developed as a result.
As the Europeans increased their presence, they involved the First Nations as guides and suppliers of furs. The Chipewyan acted as middlemen. They brought to York Factory the furs of the western tribes. The Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
, Chipewyan, Beaver and Yellowknives obtained firearms. With this new advantage, they dominated their Athapaskan neighbours, i.e. the Slavey, Sekani, and Dogrib peoples.
1800–1870
In the early 1800s, perhaps 1810, the North West Company established a post atTulita
Tulita, which in Slavey means "where the rivers or waters meet," is a hamlet in the Sahtu Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. It was formerly known as ''Fort Norman'', until 1 January 1996. It is located at the junction of the Great Bear ...
(Fort Norman) at the junction of the Mackenzie and Great Bear River
The long Great Bear River, which drains the Great Bear Lake westward through marshes into the Mackenzie River, forms an important transportation link during its four ice-free months. It originates at south-west bay of the lake. The river has ir ...
s. The site changed several times but the community of Tulita is located on the original site today.
In 1821, the North West Company and the Hudson's Bay Company merged under the name of the latter. By 1825, Sir George Simpson advanced from the junior governor in charge of the company's Northern Department to be the head of this new company. Simpson travelled throughout the north-west. For forty years he led the company. For most of that time, he made at least one major journey by canoe every year.
Exploration expeditions
 Franklin's
Franklin's Coppermine expedition
The Coppermine expedition of 1819–1822 was a British overland undertaking to survey and chart the area from Hudson Bay to the north coast of Canada, eastwards from the mouth of the Coppermine River. The expedition was organised by the Royal Nav ...
of 1819–1822 had as its goal the exploration of the northern coast of Canada, which was accessed by way of the Coppermine River
The Coppermine River is a river in the North Slave and Kitikmeot regions of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada. It is long. It rises in Lac de Gras, a small lake near Great Slave Lake, and flows generally north to Coronation Gulf, ...
. The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
expedition was organised by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
as part of its attempt to discover and map the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
. It was the first of three Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
expeditions to be led by John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through ...
, and also included George Back
Admiral Sir George Back (6 November 1796 – 23 June 1878) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer of the Canadian Arctic, naturalist and artist. He was born in Stockport.
Career
As a boy, he went to sea as a volunteer in the frigate ...
and John Richardson, both of whom would become significant Arctic explorers in their own right.
In 1825, Franklin set out on his second expedition to the Canadian North. He travelled to the mouth of the Mackenzie River and then spent the winter at Fort Franklin, now Deline, on Great Bear Lake
Great Bear Lake ( den, Sahtú; french: Grand lac de l'Ours) is a lake in the boreal forest of Canada. It is the largest lake entirely in Canada (Lake Superior and Lake Huron are larger but straddle the Canada–US border), the fourth-largest ...
.
Franklin's fateful third expedition began in 1845 and was never heard from again. A massive search followed, at first finding little trace of the expedition but resulting in the mapping of much of the Arctic coastline. It was eventually learned that Franklin had died in 1847, and the remains of the expedition's two ships were finally found in 2014 and 2016.
George Back
Admiral Sir George Back (6 November 1796 – 23 June 1878) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer of the Canadian Arctic, naturalist and artist. He was born in Stockport.
Career
As a boy, he went to sea as a volunteer in the frigate ...
, a British naval officer, naturalist and artist, served under John Franklin in his first expedition to the Arctic in 1818. On Franklin's inland Coppermine expedition of 1819–1822, Back was responsible for all the surveying and chart making. Then on the Mackenzie River expedition in 1824–1826, Back was promoted to lieutenant and then to commander.
Canadian Confederation and the late 19th century
 After the
After the Deed of Surrender
The Deed of Surrender or Rupert's Land and North-Western Territory Order is an 1870 British order in council that transferred ownership of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory from the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) to the newly created Do ...
was enacted, the United Kingdom transferred ownership of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Due to the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact boundarie ...
from the Hudson's Bay Company to the government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
. However, integration of the territories into Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Canada, Dom ...
was delayed by the Red River Rebellion
The Red River Rebellion (french: Rébellion de la rivière Rouge), also known as the Red River Resistance, Red River uprising, or First Riel Rebellion, was the sequence of events that led up to the 1869 establishment of a provisional government by ...
around the Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assiniboia, Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hud ...
. Eventually the territories were admitted into Canadian Confederation on 15 July 1870 as the North-West Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
; barring the area around the Red River Colony, which was admitted into Canadian Confederation as the province of Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
.
In 1880, the British Arctic Territories
The British Arctic Territories were a constituent region of British North America, composed of islands to the north of continental North America. They are now known as the Arctic Archipelago.
The British claim to the area was based on the di ...
was transferred from the United Kingdom to government of Canada, and was administered as a part of the North-West Territories.
Late 19th century
The first North-West Territories government sat in 1872 after theTemporary North-West Council
The Temporary North-West Council, more formally known as the Council of the Northwest Territories and by its short name as the North-West Council, lasted from the creation of Northwest Territories, Canada, in 1870 until it was dissolved in 1876. Th ...
was appointed. The first North-West Territories government sat inside the territories at Fort Livingstone for the first time in 1876. Now in Saskatchewan. The government moved to Battleford
Battleford ( 2011 population 4,065) is a small town located across the North Saskatchewan River from the City of North Battleford, in Saskatchewan, Canada.
Battleford and North Battleford are collectively referred to as "The Battlefords" b ...
in 1878. The first territorial election took place in 1881. French was abolished as an official language in 1892.
During the late-19th century, the boundaries of the territories were redefined a number of times. In 1886, the District of Keewatin's south-western border was adjusted. In 1889, the disputed area between Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
was generally granted to Ontario, with some going to the District of Keewatin, and Manitoba getting none. In 1898, following the Klondike Gold Rush, the Yukon stopped being part of the North-West Territories. A separate Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
is created from the western North-West Territories.
Treaty No. 8
 In June 1899, negotiation began on Treaty No. 8, which covered 840,000 square kilometres in the North-West Territories. It was an agreement between the Canadian Government and the Dene groups in the area in question; in return for their willingness to share their land with non-Natives, the Dene would receive medical and educational assistance, as well as treaty payments. The Canadian Government and the various Dene groups, including
In June 1899, negotiation began on Treaty No. 8, which covered 840,000 square kilometres in the North-West Territories. It was an agreement between the Canadian Government and the Dene groups in the area in question; in return for their willingness to share their land with non-Natives, the Dene would receive medical and educational assistance, as well as treaty payments. The Canadian Government and the various Dene groups, including Yellowknives
The Yellowknives, Yellow Knives, Copper Indians, Red Knives or T'atsaot'ine ( Dogrib: ''T'satsąot'ınę'') are indigenous peoples of Canada, one of the five main groups of the First Nations Dene who live in the Northwest Territories of Canada. ...
and Tłįchǫ under chief Drygeese with headmen Benaiyah and Sek'eglinan, signed the treaty in 1900 at Fort Resolution
Fort Resolution (''Denı́nu Kų́ę́'' (pronounced "deh-nih-noo-kwenh") "moose island place") is a hamlet in the South Slave Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. The community is situated at the mouth of the Slave River, on the shores o ...
(called by the Tłįchǫ ''Įndàà'') . After the signing, the group that signed the treaty was called the ''"Yellowknife B Band"'' (Helm, 7: 1994). At that point in history, Treaty No. 8 was the largest land settlement the Canadian Government had ever made (PWNHC, Historical).
20th century
In 1901, the borders of Yukon Territory were changed, gaining area from the North-West Territories.Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
separated from the territories in 1905. Although the District of Keewatin was given back to the territories, the population dropped from approx 160,000 to 17,000, of which 16,000 were aboriginal and had no right to vote under Canadian law. The government of the North-West Territories defaulted back to its 1870 constitutional status, and once again came under federal control, governed from Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
.
 In 1906, the official name dropped the hyphen, changing to "Northwest Territories".
On May 15, 1912, parts of the Northwest Territories were given to Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
In 1906, the official name dropped the hyphen, changing to "Northwest Territories".
On May 15, 1912, parts of the Northwest Territories were given to Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
Interwar period (1918–1939)
Twenty years after Treaty No. 8 was signed, oil was discovered in the Mackenzie River Valley. Upon the discovery, the Canadian Government proposed another treaty that would clear the way for miners and development of the area. The treaty was greatly debated, as the Natives did not want to lose their right to hunt, fish, gather, and trap in the area. They also opposed being "confined toIndian reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty,
that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band."
Ind ...
s." Many Dene felt that Treaty No. 8 was not honoured by the Canadian Government, and some were afraid that this treaty would turn out similarly. Nevertheless, Treaty No. 11 was signed by the Tłı̨chǫ trading chief Monfwi in the summer of 1921. The Tłı̨chǫ groups that signed this treaty were then known as the "Dog Rib Rae Band" (Helm, 7: 1994), constituting the majority of the Tłįchǫ population. Both Treaty No. 8 and Treaty No. 11 overlap in several of their boundaries, and continue to cause conflict between the two separate treaty bands (nowadays two First Nations).
In 1925, based upon the Sector Principle, Canada became the first country to extend its maritime boundaries
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Bound ...
northward to the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Mag ...
. The Northwest Territories gained in size to 3.3 million km2. This was about one third of Canada's landmass.
In the summer of 1935, nearly 1000 men grouped into 188 surveying parties covered a wide range of Canada looking for precious minerals. The most valuable discovery was made in the Yellowknife district where nearly 3,000 square miles of good gold prospecting territory was located. This brought about the town of Yellowknife
Yellowknife (; Dogrib: ) is the capital, largest community, and only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the ...
. Thirty-two years later, when the Government of the Northwest Territories came North from Ottawa, Yellowknife became the new capital.
World War II
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Canadian company Eldorado Gold Mines Ltd., which produced uranium as a byproduct of gold and radium production using ore from its mine at Port Radium
Port Radium is a mining area on the eastern shore of Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada.
It included the settlement of Cameron Bay as well as the Eldorado (also called Port Radium) and Echo Bay mines. The name Port Radium did n ...
in the Northwest Territories, was recruited by the Canadian government to assist in procuring uranium for the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
. The ores were shipped from the Eldorado Mine to Port Hope, Ontario to be processed.
Between 1942 and 1946, forty thousand American military and civilian personnel came to the Canadian north-west; invited by the Canadian government. Plans called for the